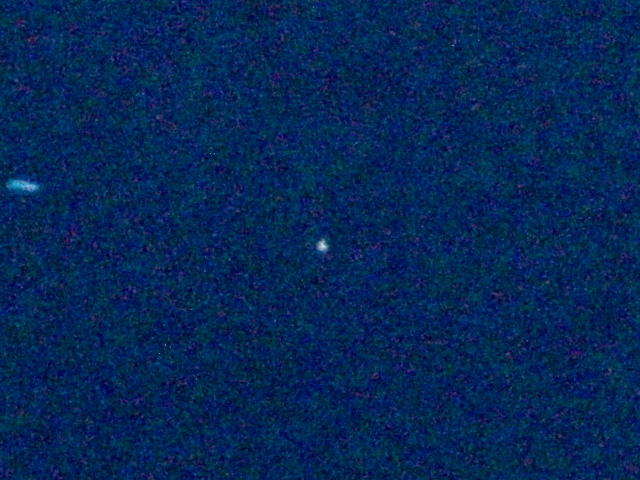
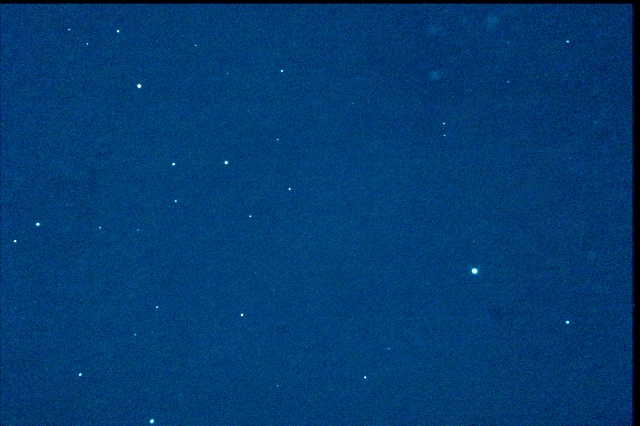

2019/03/31T22:06:36〜22:29:06までの30秒間露光20枚を合成
小惑星(1185)日光 Nikko
露光時間:30秒*20=10分 t-T=+26秒
Mewlon210FR/2050mm + LPS-P2 + 60D/ISO3200 / EM200Temma2
フラット補正済
StellaImage6.5で加算合成、レベル補正とリサイズ
|
小惑星1266番 利根 (1266)Tone
|
|
1185 Nikko From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Jump to navigation Jump to search 1185 NikkoDiscovery?[1] Discovered by O. Oikawa Discovery site Tokyo Astronomical Obs. (389) Discovery date 17 November 1927 Designations MPC designation (1185) Nikko Named after Nikko (Japanese city)[2] Alternative designations 1927 WC ・ 1930 SE1 1930 SG1 ・ 1930 SH1 Minor planet category main-belt ・ (inner)?[3] Orbital characteristics?[1] Epoch 4 September 2017 (JD 2458000.5) Uncertainty parameter 0 Observation arc 86.78 yr (31,697 days) Aphelion 2.4744 AU Perihelion 2.0006 AU Semi-major axis 2.2375 AU Eccentricity 0.1059 Orbital period 3.35 yr (1,222 days) Mean anomaly 280.93° Mean motion 0° 17m 40.2s / day Inclination 5.7013° Longitude of ascending node 71.904° Argument of perihelion 1.9614° Physical characteristicsDimensions 8.347±0.297 km[4] 11.35 km (calculated)[3] 12.56±0.83 km[5] Rotation period 3.781±0.0326[6] 3.78615±0.00005 h[7] 3.788±0.0326 h[6] 3.7889±0.0004 h[8] 3.79±0.01 h[9] 3.792±0.002 h[8] Geometric albedo 0.164±0.023[5] 0.20 (assumed)[3] 0.370±0.041[4] Spectral type S (Tholen)[1] ・ S (SMASS)[1] S?[3] B?V = 0.923[1] U?B = 0.514[1] Absolute magnitude (H) 11.674±0.002 (R)[6] ・ 11.99±0.33[10] ・ 12.09[1][3][4][5] 1185 Nikko, provisional designation 1927 WC, is a stony asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 10 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 17 November 1927 by Okuro Oikawa at the Tokyo Astronomical Observatory, Japan.[11] The asteroid was named after the Japanese city of Nikk?.[2] Orbit and classification Nikko orbits the Sun in the inner main-belt at a distance of 2.0?2.5 AU once every 3 years and 4 months (1,222 days). Its orbit has an eccentricity of 0.11 and an inclination of 6° with respect to the ecliptic.[1] Nikko's observation arc begins with its first used observation taken at Johannesburg Observatory in 1930, or 3 years after its official discovery observation at Tokyo.[11] Physical characteristics In both the Tholen and SMASS taxonomy, Nikko is a common stony S-type asteroid.[1] Rotation period Between 2004 and 2011, several rotational lightcurves of Nikko were obtained from photometric observations taken by astronomers Laurent Bernasconi,[8] Hiromi and Hiroko Hamanowa,[8] John Menke,[12] Robert Stephens,[9] as well as at the Palomar Transient Factory in California.[6] Lightcurve analysis gave a rotation period between 3.781 and 3.792 hours with a brightness variation between 0.26 and 0.50 magnitude (U=3/3/3/3-/2/2).[3] Diameter and albedo According to the survey carried out by the Japanese Akari satellite and NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer with its subsequent NEOWISE mission, Nikko measures 8.347 and 12.56 kilometers in diameter, and its surface has an albedo of 0.370 and 0.164, respectively.[4][5] The Collaborative Asteroid Lightcurve Link assumes a standard albedo for stony asteroids of 0.20 and calculates a diameter of 11.35 kilometers with an absolute magnitude of 12.09.[3] Naming This minor planet was named for the Japanese city of Nikk?, located in the Tochigi Prefecture of central Japan. The tourist resort is known for its Shinto shrine and a UNESCO World Heritage Site Nikk? T?sh?-g?. The official naming citation was published by Paul Herget in The Names of the Minor Planets in 1955 (H 110)[2][13] |
2019年03月31日 15.2等











